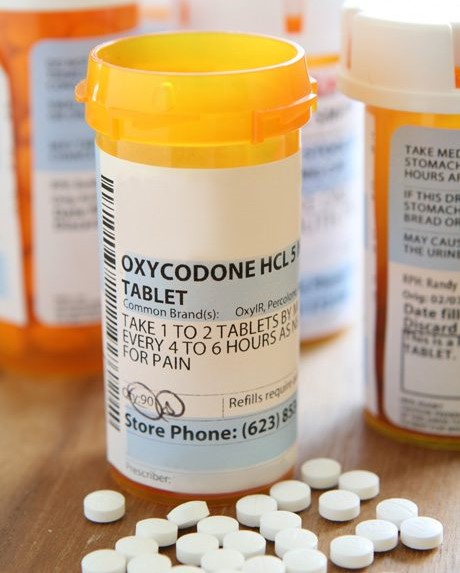
Oxycodone Tablets
Oxycodone tablets are a prescription-only pain relief medication widely used in the treatment of moderate to severe acute or chronic pain. As a powerful opioid analgesic, Oxycodone is part of the narcotic class of medications that act directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to reduce the perception of pain. This makes it a common treatment choice for patients recovering from surgery, those with long-term conditions such as cancer pain, or individuals who have not responded to over-the-counter pain relievers.
What is Oxycodone?
Oxycodone is a semi-synthetic opioid derived from thebaine, a naturally occurring alkaloid of the opium poppy. It is available in both immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (ER) formulations. Immediate-release Oxycodone provides fast pain relief, typically within 30 minutes, while extended-release tablets deliver a controlled dose over 12 to 24 hours for long-term pain management.
Common Uses of Oxycodone Tablets
-
Post-surgical pain management – after operations or major medical procedures.
-
Chronic pain conditions – including arthritis, cancer-related pain, and severe musculoskeletal conditions.
-
Injury-related pain – fractures, trauma, or nerve pain.
-
Palliative care – supporting patients with life-limiting illnesses to manage ongoing pain.
How Oxycodone Works
Oxycodone works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord. By activating these receptors, it blocks pain signals from being transmitted to the brain, while also producing a feeling of relaxation and well-being. This powerful mechanism is why Oxycodone is often prescribed when standard painkillers such as ibuprofen, paracetamol (acetaminophen), or aspirin are not effective.
Dosage & Administration
-
Immediate-release tablets are usually taken every 4–6 hours as needed.
-
Extended-release tablets are generally taken every 12 hours, depending on a doctor’s prescription.
-
Dosage varies based on the patient’s age, weight, medical history, and level of pain.
-
Oxycodone must always be taken exactly as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Side Effects & Safety Information
Like all opioids, Oxycodone carries risks and possible side effects. Common side effects include:
-
Nausea, vomiting, or constipation
-
Drowsiness and dizziness
-
Dry mouth
-
Sweating or itching
More serious side effects can include slowed breathing, confusion, low blood pressure, or risk of dependency. Patients should never combine Oxycodone with alcohol, sedatives, or other opioids unless advised by their doctor, as this can increase the risk of dangerous respiratory depression.
Precautions & Warnings
-
Addiction and dependency: Oxycodone is a controlled substance with a high risk of misuse. It should only be taken under strict medical supervision.
-
Pregnancy & breastfeeding: Oxycodone may cause withdrawal symptoms in newborns and should be avoided unless essential.
-
Driving & operating machinery: Due to its sedative effects, patients should not drive until they know how Oxycodone affects them.
-
Drug interactions: Antidepressants, benzodiazepines, and alcohol may amplify side effects.
Differences Between Oxycodone and Other Painkillers
Many patients compare Oxycodone vs. Hydrocodone, Oxycodone vs. Morphine, or Oxycodone vs. OxyContin. While similar in action, Oxycodone is often considered slightly more potent than Hydrocodone. OxyContin is simply a brand name for the extended-release form of Oxycodone.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.